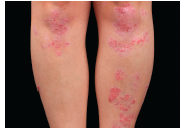
The etiology of the underlying inflammation-associated pigmentation changes in psoriasis was studied in this article. Previously, it was unclear how the myriad of cytokines known to be involved in inflammatory skin processes affect epidermal melanocytes. The authors sought to determine how IL-17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) influence normal human melanocytes, as these two cytokines have been implicated in various skin diseases. IL-17 and TNF jointly stimulated broad inductions of cytokines, including melanoma mitogens CXCL1 and IL-8. Moreover IL-17 and TNF synergistically inhibited pigmentation-related signaling and melanin production, and induced keratinocyte production of β-defensin 3, an antagonist for melanocortin 1 receptor. When analyzing psoriasis lesions that are known to overexpress IL-17 and TNF, the authors observed an increase in melanocyte number and a simultaneous decrease in pigmentation signaling. Furthermore, therapeutic neutralization of TNF and IL-17 with mAbs resulted in a rapid recovery of pigment gene expression in psoriasis lesions. They conclude that IL-17 and TNF can affect both the growth and pigment production of melanocytes, which may contribute to the pigmentation changes associated with psoriasis. These findings may allow the development of novel therapeutics for pigmentary disorders and bring new insights into the immune milieu surrounding melanocytes and related neoplasms. J Invest Dermatol. December 2013. PMID: 23732752.
© 2026 IHR Magazine | Canada's Natural Health Industry Authority | Le guide de l’industrie canadienne de la santé naturelle